Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) is a way for teams and organizations to reflect and ask themselves, “How are we doing?” and “How can we do it better?” CQI provides a process for the intentional use of evidence to critically assess performance, identify strengths and areas needing improvement, identify solutions, and monitor those solutions in an environment that embraces continuous learning.
OhioKAN’s CQI framework is grounded in the principles and common language of CQI, as outlined by Chapin Hall and the Center for State Child Welfare Data
61
. These principles, while originally designed for child welfare CQI systems and applied in states’ implementation of the Family First Prevention Services Act, have been tailored to OhioKAN’s unique model and include:
- Viewing CQI as a cyclical Plan-Do-Study-Act process with problem-solving activities,
- Valuing and incorporating rigorous use of evidence at every stage,
- Developing and testing hypotheses that are rooted in OhioKAN's theory of change and through the lens of OhioKAN's Inclusion, Diversity, Equity and Access (IDEA) Framework,
- Converting data to evidence,
- Focusing on the variety of experiences and outcomes of children and families served,
- Continually using a data-driven, strategic, and systematic approach to adjust process, quality, and/or capacity investments,
- Incorporating continuous learning and improvement in everyday practice,
- Engaging and empowering staff toward common goals and leveraging their expertise to achieve program goals,
- Examining service delivery processes through performance measures, and
- Communicating well throughout the organization.
OhioKAN CQI Approach
OhioKAN’s CQI approach provides the framework for improvement planning and ongoing monitoring of the program’s key performance, practice, and implementation measures. CQI activities ensure quality service delivery and effective program implementation to achieve OhioKAN’s vision for kinship and adoptive families. CQI practices are present throughout the model and reinforced through OhioKAN’s culture of continuous learning, staff reflect on practice and apply CQI principles throughout every aspect of the program in both the family and community pathways of the theory of change.
The OhioKAN CQI framework collects, aggregates, analyzes, and compares program data within and across the state’s ten regions and two implementation cohorts to fully leverage implementation data and improve program delivery. This framework creates opportunities for the OhioKAN program to be implemented with greater effectiveness and responsiveness to the needs of kinship and adoptive families it serves. A comprehensive CQI measurement framework tracks implementation and performance outcomes and identifies opportunities to improve practice and service delivery. The monthly CQI Dashboard informed by the measurement framework is regularly reviewed by coaches and regional directors and further discussed during monthly CQI Process Team meetings. By promoting consistent implementation of the OhioKAN model across the state, OhioKAN CQI not only monitors program fidelity, but also program quality for and inclusion of OhioKAN families.
Regular CQI activities allow staff to learn and build upon effective outreach strategies for eligible families, understand OhioKAN family satisfaction, strengthen practice skills, grow available and inclusive services, and supports to meet families’ diverse needs, ensure fidelity to the model at all levels of the intervention, and identify additional community resources to invest and achieve OhioKAN outcomes. CQI implementation supports, such as training, procedures, meeting facilitation, practice profiles, practice observation rubrics, monitoring tools and guides, and reporting structures, continue to be refreshed and refined in collaboration with OhioKAN implementation and evaluation partners as the OhioKAN program grows and staff become proficient in the improvement cycles.
The OhioKAN CQI approach incorporates the OhioKAN Inclusion, Diversity, Equity and Access (IDEA) Framework. OhioKAN believes that equity is not only a value and desired outcome, but a process of intentional action to eliminate systemic barriers that have produced historical and contemporary inequities based on race, gender, class, sexual orientation, geography, and other forms of difference. Such actions within CQI include the disaggregation of data by the forms of difference listed. In reference to the OhioKAN theory of change, the disaggregation of data can be used on the family track to better improve service delivery for the diverse communities served and through the community track by linking data disaggregated by race and geography to identify systemic barriers for certain communities in Ohio. Through the disaggregation of CQI data, OhioKAN staff is equipped with a robust set of data to better inform decision-making and improvements around service delivery at both the family and community level.
OhioKAN is committed to partnering with families served at all levels of their involvement with the program. OhioKAN recognizes that families are experts of their own experience and are fully equipped to identify program improvement strategies. Families and those with lived experience inform improvement planning within OhioKAN through surveys, focus groups and Regional Advisory Councils.
OhioKAN CQI, Evaluation, and Performance Management
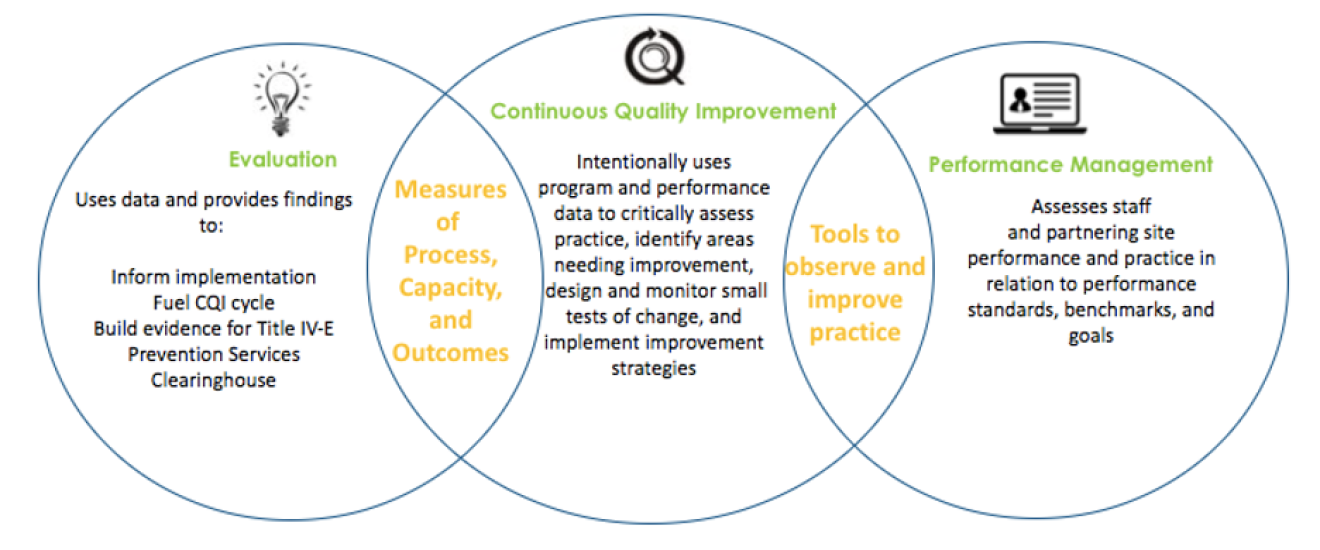
Figure 7: Relationship between OhioKAN CQI, Evaluation, and Performance Management
As shown in figure 7, OhioKAN CQI is closely aligned with the program’s evaluation activities and performance management framework. The findings from evaluation activities not only inform course corrections and build the evidence base for OhioKAN, but also fuel the CQI cycle. Similarly, CQI and performance management both assess staff and partnering site practice skills and use the same tools to observe and improve practice. While related to CQI, evaluation and performance management each represent distinct frameworks, whose relationships with CQI are further explained below.
CQI and Evaluation
The OhioKAN CQI and Evaluation efforts, as shown in figure 1, are interconnected and contribute to OhioKAN’s culture of continuous learning. OhioKAN’s evaluation process is a comprehensive, rigorous approach to assess the model's readiness for implementation and its effectiveness. Evaluation activities are focused on answering key research questions related to the model's implementation, evaluability, usability, and effectiveness in addition to site readiness. These evaluation activities will provide insight on whether OhioKAN is effective at achieving desired outcomes, for which populations, and under which circumstances. By building this evidence for OhioKAN’s impact, evaluation efforts will contribute to the larger field’s learning for effective kinship and adoptive family interventions. Ultimately, the findings from the effectiveness trial will support OhioKAN’s rating on the Title IV-E Prevention Services Clearinghouse. Many of the same measures of process, capacity, and outcomes feed CQI and evaluation activities, and evaluation findings fuel the CQI process. To complement evaluation initiatives, the OhioKAN CQI framework ensures consistent implementation of the model through ongoing monitoring of key reach, fidelity, quality, and outcome indicators. CQI and evaluation activities inform program refinements and implementation course corrections to strengthen the model and ensure its sustainability.
CQI and Performance Management
While OhioKAN’s CQI processes and performance management practices are closely interrelated, as seen in figure 7, they represent distinct frameworks. OhioKAN’s CQI framework is focused on the intentional use of data to critically assess practice to identify and monitor solutions. OhioKAN’s Performance Management Framework provides an additional set of levers to influence staff and partnering site performance and establish a culture of accountability through its structured supervision and performance assessment processes. Staff and sites are continuously monitored through supervision practices to assess their ability to meet role expectations and performance goals. These performance assessments also inform decisions related to professional development, staffing, and site contracting. The Performance Management Framework complements OhioKAN CQI through its organizing principles:
- Promote information-based decision-making
- Embed CQI in routine management practices
- Provide easy access to information
Both CQI and performance management leverage the same tools and meeting spaces to observe and monitor staff performance and practice. These include tools to observe practice as well as case-level data reports in SACWIS. While OhioKAN’s CQI framework uses these tools to fuel improvement cycles, the Performance Management Framework apply them to evaluate individual staff and partnering site performance. CQI is not intended to replace supervision, but to enhance it by discussing job performance feedback and working with staff to strengthen skills at regular supervisory meetings or coaching sessions. During regular all-staff and management meetings, CQI-related agenda items are routinely discussed. In alignment with the Performance Management Framework’s organizing principles and in keeping with OhioKAN’s culture of continuous learning, staff apply CQI practices during supervisory and management meetings to identify performance areas needing improvement and develop strategies to refine skills. For more on OhioKAN performance management, please see the Performance Management Framework.
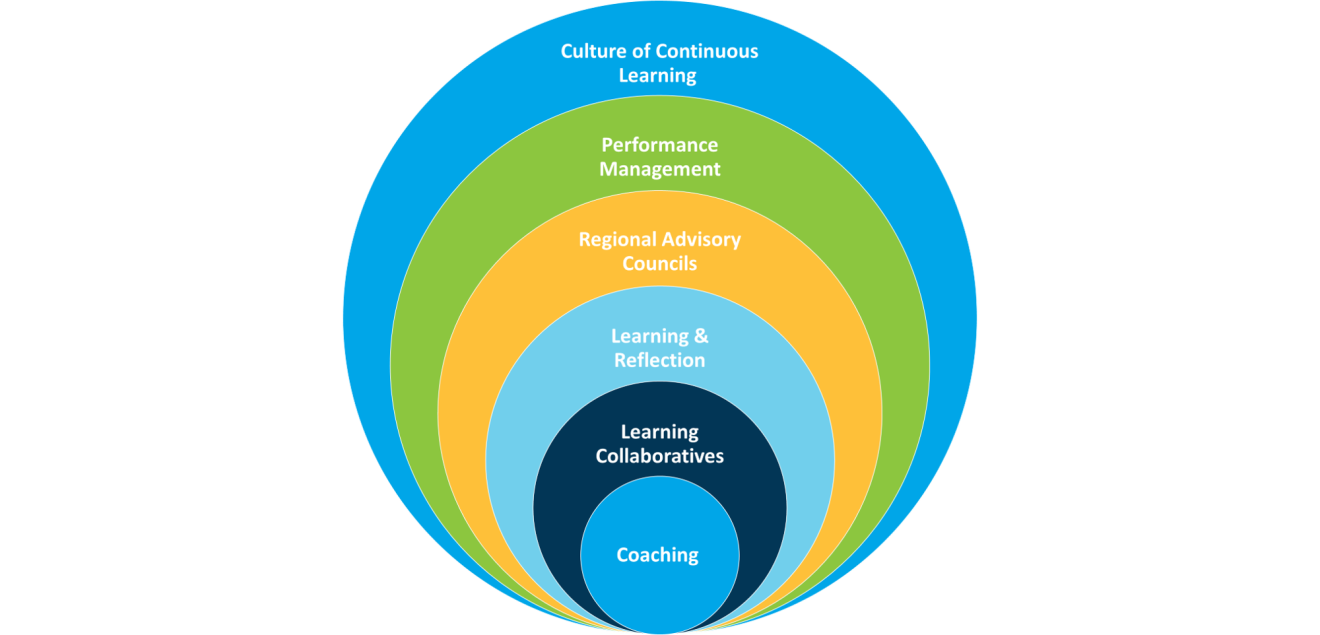
OhioKAN Culture of Continuous Learning
Figure 8: OhioKAN Spheres of Continuous Learning, which includes the areas in which CQI occurs throughout the program.
OhioKAN is dedicated to creating a culture of continuous learning, grounded in the belief that all individuals involved in OhioKAN play a role in improvement cycles. OhioKAN’s environment of continuous learning provides space for staff, community partners, and families to learn from each other on a daily basis and at every stage of the model. The “spheres of continuous learning” in figure 8 above refer to the different dimensions of the OhioKAN program, with the largest sphere representing the culture of continuous learning that is present throughout all aspects of the program. Within each sphere, staff leverage CQI practices to discuss performance challenges, assess program outcomes, and elicit feedback from families, each other, and community stakeholders to inform and co-create improvement strategies. OhioKAN’s culture of learning is promoted and sustained through each sphere’s use of CQI practices, which contribute to the larger OhioKAN CQI process. The individual spheres are further explained below:
- Performance Management: This sphere encompasses the learning within team, supervisory, and partnering site relationships that occurs as part of OhioKAN’s infrastructure for monitoring and managing staff and partnering site performance.
- Regional Advisory Councils: This sphere encompasses the learning within each region’s community as part of OhioKAN’s Regional Advisory Council structure.
- Learning and Reflection Sessions: This sphere encompasses the opportunity for cohort staff to engage in informal conversation around performance and programmatic strengths, challenges and questions
- Learning Collaboratives: This sphere encompasses the peer learning between program staff in each cohort as part of the OhioKAN Learning Collaborative framework.
- Coaching: This sphere encompasses the learning between coaches and staff providing navigation services during regular coaching sessions.
Each sphere’s feedback loops promote learning and improvement between program staff, OhioKAN families, and stakeholders across all regions. Supervisory and management meetings, reporting, and communication procedures facilitate these feedback loops and support the CQI process. Insight from a diverse group of families, stakeholders and frontline staff can inform necessary changes to improve the quality and equity of services, staff behaviors, fidelity to the OhioKAN model, and community service array gaps. The feedback loops and insights from stakeholders reinforce OhioKAN’s culture of continuous learning where CQI principles are practiced on a regular basis and incorporated in everyday conversations.
Elements of OhioKAN’s CQI infrastructure, such as data monitoring tools, reporting mechanisms, CQI practices outlined in the CQI Toolkit, and performance measures, are leveraged and operationalized within each sphere by staff, community, and family participation in OhioKAN’s CQI process. Members of each sphere use small-scale cycles of plan-do-study-act (PDSA), as shown in figure 8, to identify, implement, and monitor tests of change to inform service delivery and implementation improvement strategies.
- 61Wulczyn, F., Alpert, L., Orlebeke, B., & Haight, J. (2014). ‘Principles, language, and shared meaning: Toward a common understanding of CQI in Children Services.” Chapin Hall at the University of Chicago.